SD vs HD vs Full HD: What's the Difference?

In today's digital age, live streaming has become a common medium for sharing events, live webinars, gaming sessions, live quiz sessions, and more. One of the crucial factors determining the quality of a live stream is its resolution. The three most commonly used resolution standards are Standard Definition (SD), High Definition (HD), and Full High Definition (FullHD). Each comes with its own set of advantages and considerations, making it essential to understand their differences and use cases.
SD vs HD Differences
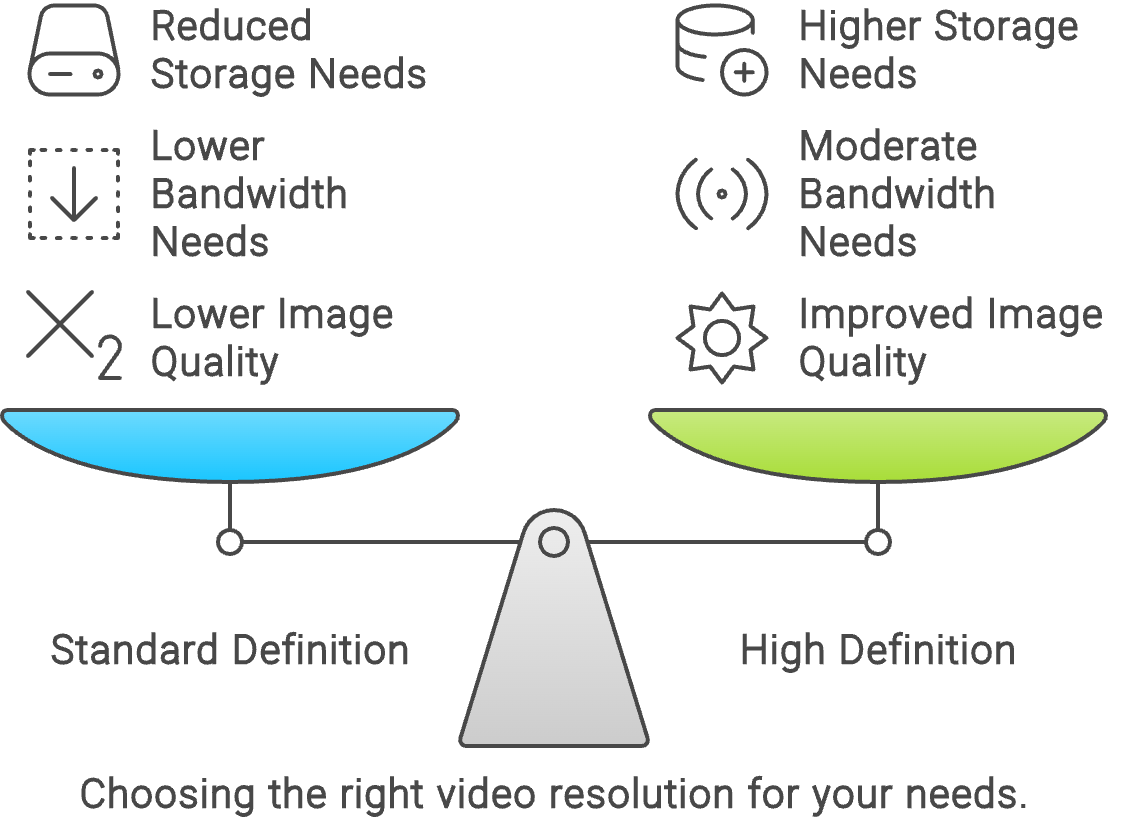
The main differences between SD (Standard Definition) and HD (High Definition) are resolution and picture quality. SD typically has a resolution of 480p, resulting in lower clarity and detail. HD offers higher resolution options (720p, 1080p), providing sharper, crisper images with improved color and finer details.
HD vs Full HD Differences
The main distinctions between HD and Full HD are resolution and image quality. HD typically has a resolution of 1280x720 pixels (720p), while Full HD features 1920x1080 pixels (1080p). Full HD provides crisper and more detailed images compared to HD, making it better for larger screens and enhanced viewing experiences.

Detailed Comparison of SD vs HD vs Full HD
Standard Definition (SD)
Resolution.
- Typically at 640x480 pixels (often referred to as 480p).
Advantages ✅
- Lower Bandwidth Requirements: SD streams require significantly less bandwidth compared to HD and FullHD. This makes it accessible to viewers with slower internet connections.
- Reduced Storage Needs: With lower resolution, SD streams consume less storage space. This can be beneficial for creators who need to archive a large volume of content.
- Compatibility: SD is compatible with a wide range of older devices that may not support higher resolutions.
Disadvantages 🙁
- Lower Image Quality: The primary downside of SD is its lower image quality. Text may appear blurry, and fine details can be lost, which can be particularly problematic for content that benefits from visual clarity, such as gameplay or instructional videos.
High Definition (HD)
Resolution:
- Typically at 1280x720 pixels (720p).
Advantages ✅
- Improved Quality: HD offers a noticeable improvement in image sharpness and clarity compared to SD. This makes for a more enjoyable viewing experience.
- Moderate Bandwidth: While HD requires more bandwidth than SD, it is still manageable for many users with average internet speeds.
- Better Detail and Text Clarity: Textual content and fine details become clearer, making HD suitable for educational content, presentations, and most gaming streams.
Disadvantages 🙁
- Increased Bandwidth Usage: HD streams require more bandwidth, which might not be feasible for viewers with limited internet speed or data caps.
- Higher Storage Requirements: Archiving HD content consumes more storage space compared to SD, which can be a consideration for long-term content storage.
Full High Definition (FullHD)
Resolution:
- Typically at 1920x1080 pixels (1080p).
Advantages ✅
- Superior Image Quality: FullHD provides the best image clarity and detail among the three options, offering an immersive viewing experience. This is particularly beneficial for content that thrives on visual richness, such as high-end gaming, live events, and professional broadcasts.
- Professional Standard: FullHD is widely regarded as the professional standard for modern live streaming, setting the benchmark for quality that many viewers have come to expect.
- Greater Audience Engagement: High-quality streams can lead to better audience engagement and satisfaction, potentially increasing viewership and retention rates.
Disadvantages 🙁
- High Bandwidth Requirement: Streaming in FullHD demands a robust and stable internet connection. Viewers with slower internet speeds may experience buffering or be unable to watch the stream seamlessly.
- Significant Storage Needs: Archiving FullHD content requires substantial storage capacity, which can be costly and cumbersome over time. Using conventional means like cleanup tools is hardly sufficient to maintain enough free space.
- Higher Processing Needs: Broadcasting in FullHD puts more strain on both the streaming hardware and the viewers' devices, necessitating more powerful equipment.
With Livereacting, you can stream your videos as live in Full HD quality. This platform allows creators to engage with their audience through high-definition video streaming, ensuring a professional and polished look.
Summary
In summary, choosing between SD, HD, and FullHD for live streaming depends on the specific needs and constraints of the streamer and the audience. If you cater to a broad audience with varying internet speeds and older devices, SD might be the most inclusive option. For more quality-conscious content, HD provides a good balance between quality and resource demand. However, if you aim to deliver the best possible viewing experience and have the necessary infrastructure, FullHD is the gold standard.
Understanding these differences helps in making informed decisions, optimizing both the streaming quality and the viewer experience. Whether you're a novice content creator or an established broadcaster, tailoring your streaming setup to match your and your audience’s needs will enhance the overall impact of your live streams.
Transform Your Live Streams with LiveReacting
Join 10,000+ streamers who are boosting engagement and viewership by adding pre-recorded videos, games, polls, and countdowns to their streams.
Try LiveReacting for free today and take your streams to the next level!
